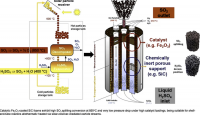
Abstract: Catalytic sulphur trioxide splitting is the highest-temperature (850–900 °C), endothermic step of several sulphur-based thermochemical cycles targeted to production of hydrogen or solid sulphur. The demonstrated capability of centrifugal particle solar receivers of heating particle streams at such temperatures, can allow for “allothermal” implementation of this step via the enthalpy of such particle streams in … Continue reading Published at Applied Catalysis – Structured sulphur trioxide splitting catalytic systems and allothermally-heated reactors for the implementation of Sulphur-based thermochemical cycles via a centrifugal solar particle receiver