General Coordination: Esther Rojas, CIEMAT, Spain
If you are willing to participate in any of the following Activity Lines, do not hesitate to get in contact with the corresponding coordinator of the activity or with Esther Rojas (general coordinator)
Objective
Promoting collaboration on Thermal Energy Storage (TES) to improve its reliability, integration on CSP plants and to develop a common language.
Current Activity Lines
Characterization of Specific Equipment for Commercial TES
Coordinator: M. Rodriguez, CIEMAT, Spain
Motivation:
-
- Components reliability is not proved before installing them at plants.
- In commercial plants if one of these components presents a malfunction, it will just be repaired (often by component replacement)
Aligned with task 6.4 of the European project SFERA-III
- Dissemination activities funded by MOSAICO Project Towards the standardization of molten salt loops, instrumentation and components)
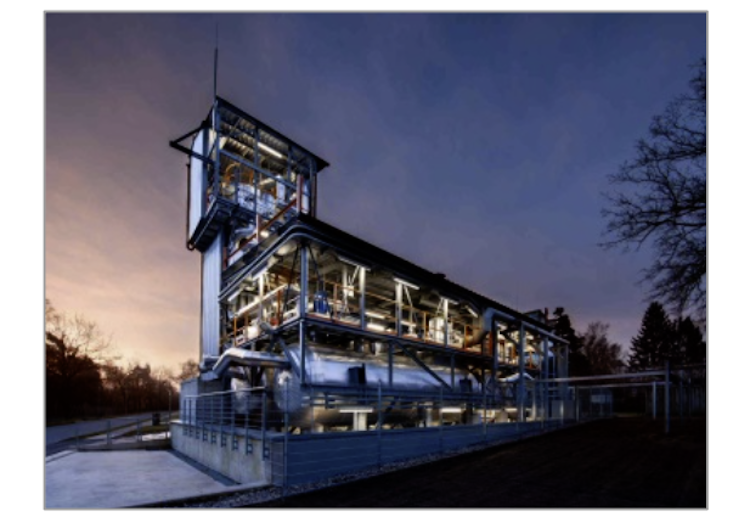
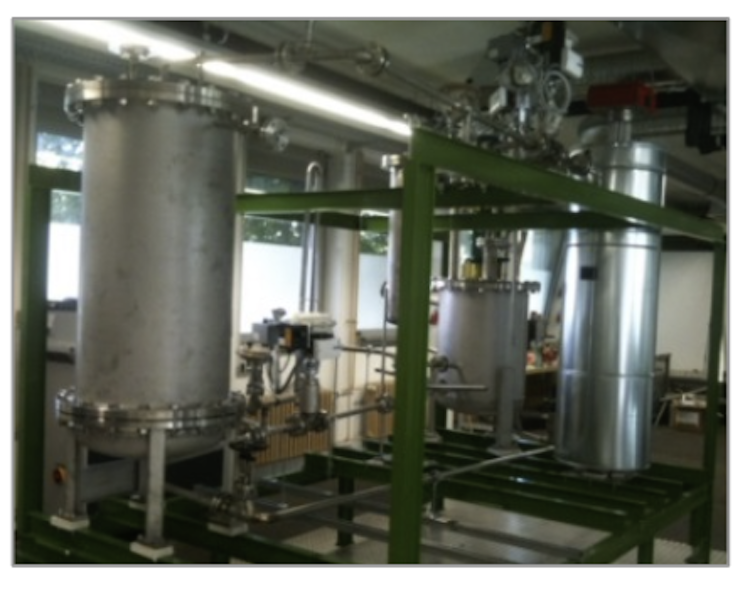
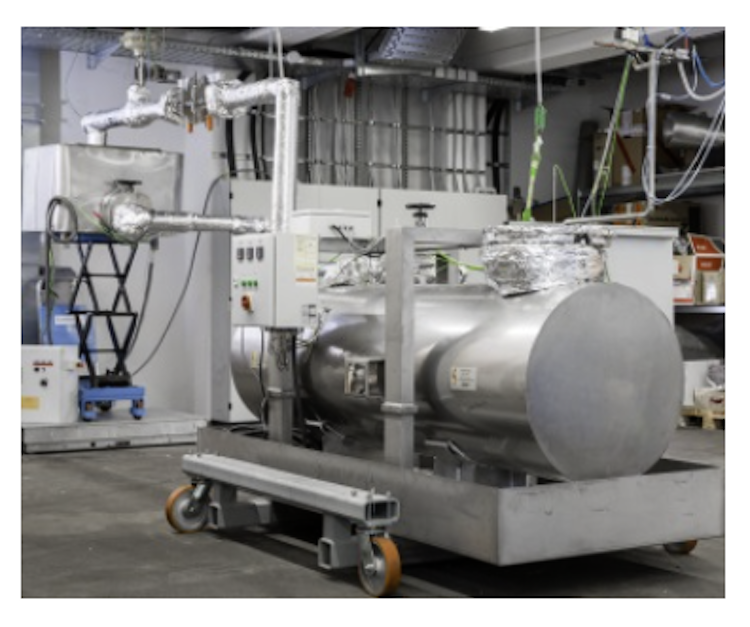
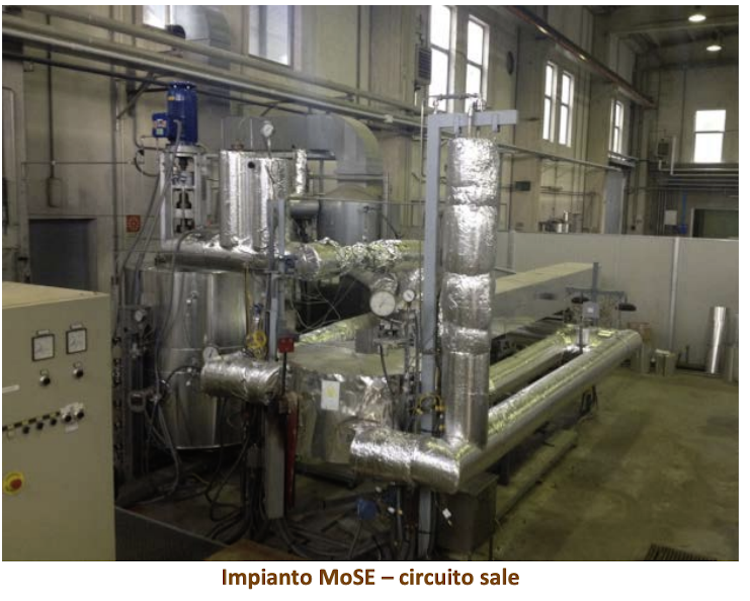
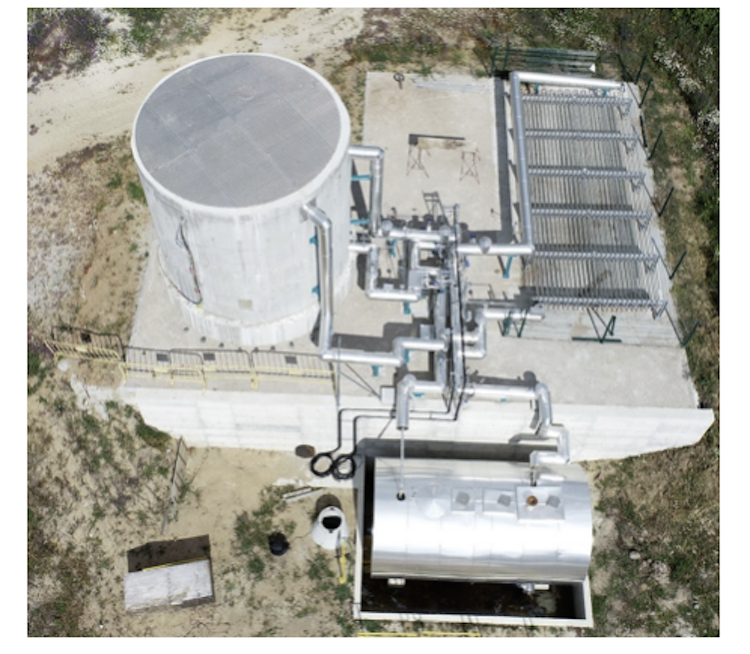
Partners and facilities currently involved:
Partner
Facility
Capability of testing



Valves, flowmeters, HX, vertical pumps, pressure transducers

Valves, flowmeters, parabolic trough receivers, pressure transducers

Valves, flowmeters, pressure transducers, strain gauges

Valves, flowmeters, parabolic trough receivers, flexible joints, pressure transducers

Valves, flowmeters, pressure transducers, Heat tracing, Heating elements, HX, parabolic trough receivers
Current status:
- Identification of critical equipment and related problems (open to new problems that could appear in commercial plants)
- Definition of tests.
- Tests on valves, flanges, flowmeters, heating elements, pressure sensors and flexible joints.
- MOSAICO project, funded by SolarPACES TCP and coordinated by M. Rodriguez (CIEMAT). This project joint the efforts performed in this activity line with those of the SFERA III project to present the testing methodologies to the industrial sector.
- In the workshop entitled Towards the standardization of molten salt loops’ instrumentation and components, celebrated in Evora, October, the 24th, 2023, the main results were presented:
1. SolarPACES Task III and SFERA-III project introduction (by M. Rodriguez, CIEMAT, and M. Georgiou, CYI)
2. Facilities for characterization of componentsMOSAICO: TESIS (M. Prenzel, DLR)
MOSA and BESis Facilities at Ciemat (M. Rodriguez, CIEMAT)
PROTEAS (M. Georgiou, CYI)
Fraunhofer ISE infrastructure for Molten Salt (by T. Fluri, Fraunhofer-ISE)
ENEA’s Facilities (W. Gaggioli, ENEA)
EMSP Facility (P. Horta, UEvora)3. Valves characterisation (M. Rodriguez, CIEMAT and W. Gaggioli, ENEA)
4. Pressure sensors characterisation (M. Rodriguez, CIEMAT)
5. Flow meters characterisation (T. Fluri, Fraunhofer-ISE)
6. Electrical heat tracing characterization (W. Gaggioli, ENEA, and M. Georgious, CYI)
7. Integration of components in a 3.6MW molten salt plant (P. Horta, UEvora)
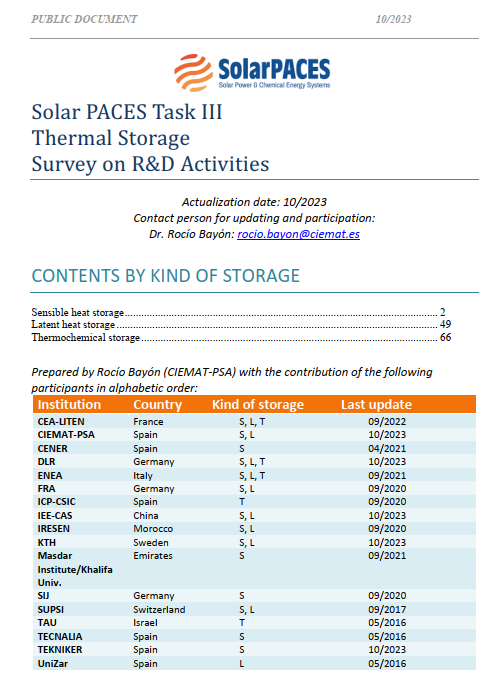
Survey of R&D Activities on Thermal Storage Systems
Coordinator: R. Bayón, CIEMAT, Spain
Motivation: Promoting current research activities on TES by creating a database containing information of R&D activities in thermal storage developed by the participants
Current Status: Survey of current participants updated 9/2022. (Next update: September 2024)Previous Activity Lines
Storage Materials
Coordinators: J. Nieto (Tecnalia/Spain), J. González (IMDEA Energía/Spain)
Main Achievements: 3 Round Robin Tests performed:- Specific heat capacity of sensible materials (Solar salt with nanoparticles) 9 participants, including industry; Achieved agreement in accurately measuring cp with DSC, according to normalized methods ASTM E1269 and MDSCTM in the range of temperatures 200 and 400ºC (SolarPACES 2016).
- Reaction enthalpy of thermochemical materials.
- Cobalt oxide: 7 participants, including industry; there was no coherency and agreement in the results obtained by different partners (SolarPACES2016).
- Perovskites: 7 participants; Some discrepancies in results (SolarPACES2018).
Prototype Testing
Coordinator: P. Garcia, CEA, France
Main Achievements- Report Definition of common procedures for testing thermal storage prototypes for STE plants (2016).
- Aligned with task 6.3 of the European project SFERA-III: D6.3 Protocol for testing sensible and latent storage prototypes. Main results presented at IRES 2022 in the Workshop Towards a fair evaluation of Thermal Energy Storage prototypes – Guidelines for CSP applications:
- Why do research and industry need KPI definitions and test procedures? presented by P. Azevedo (LNEG)
- Case studies on sensible heat storage, presented by J. Weiss (Fraunhofer ISE)
- Case studies on latent heat storage, presented by P. Garcia (CEA)
- Case studies on thermal losses calculations, presented by R. Liberatore (ENEA)