Published in the January Issue of Energy Conversion and Management
Abstract
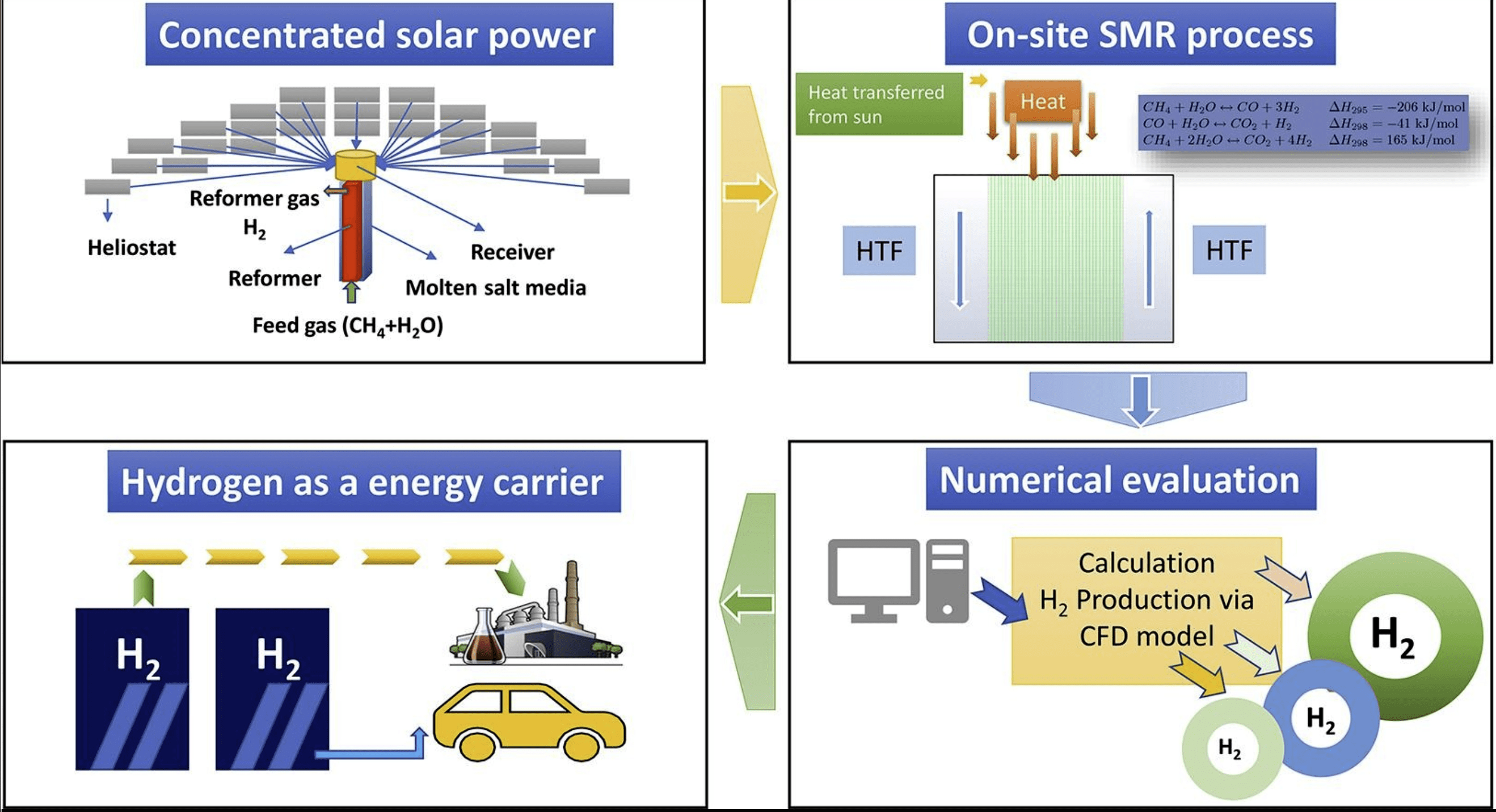
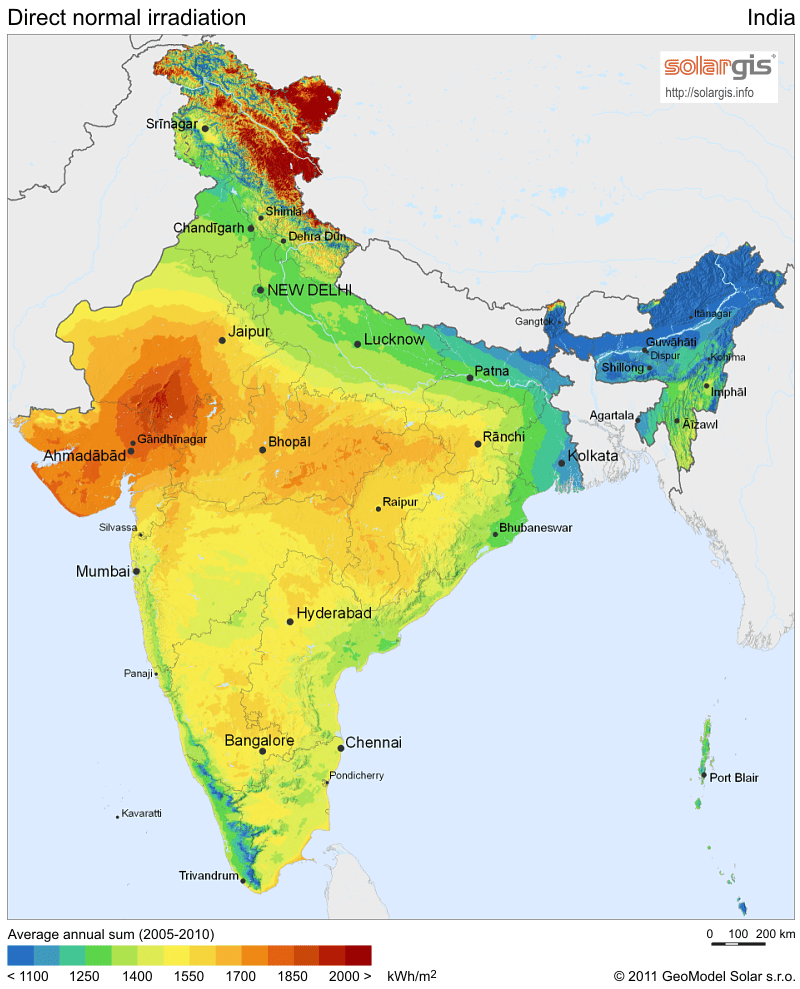
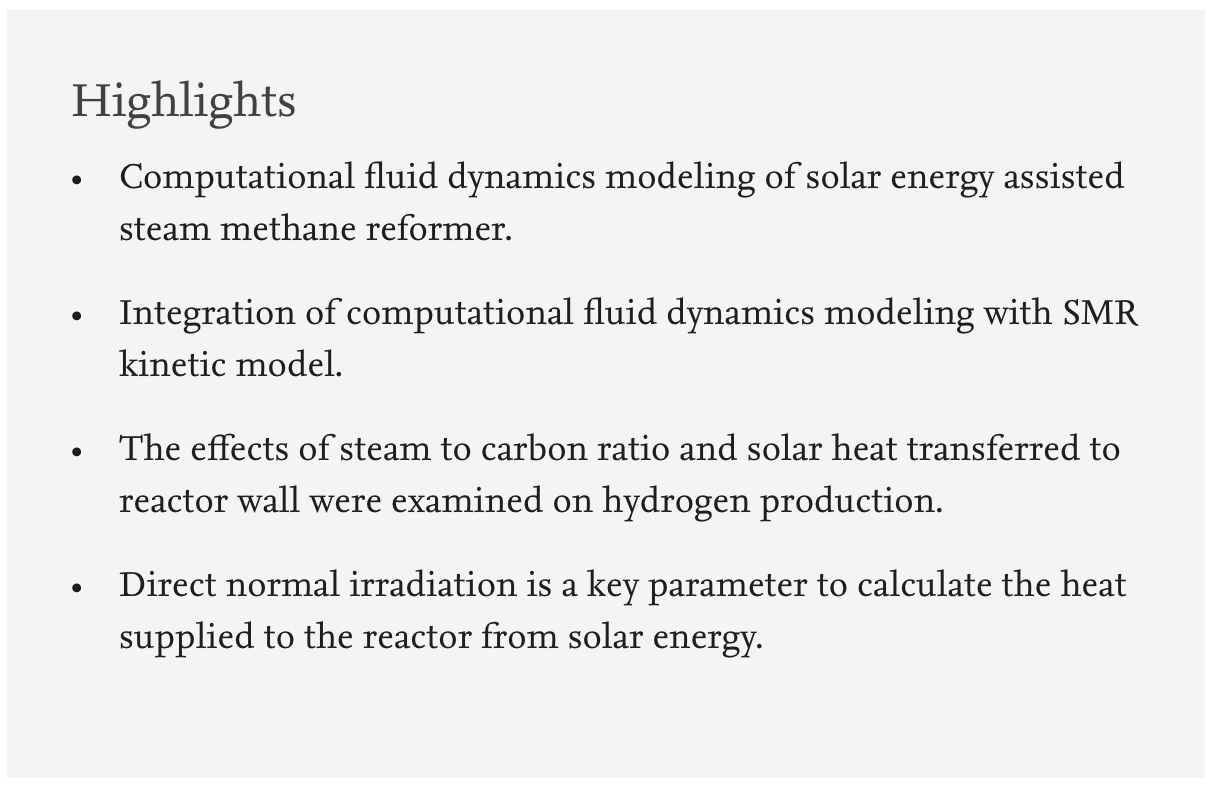
The purpose of this paper is to study the performance of the steam methane reformer (SMR) using solar energy as a heat source using a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) model. An analysis of the flow and heat transfer performance of scaled-up SMR with solar radiation is conducted using a CFD model. The reactor was operated under the predefined thermal conditions (800–1000 K) and steam to carbon ratio (S/C = 2.0–4.0) in order to investigate the effects of operating parameters on hydrogen production. The results indicated that the mass ratio of feed gas and temperature have a significant effect on methane conversion ratio, total hydrogen yield, and composition of reformate gas. Under the operating conditions of S/C = 4.0, 1000 K, 506.5 kPa, the highest CH4 conversion of methane gas is %99.78. The total hydrogen energy yield is 2.41 at this point. In this study, it is also demonstrated that concentrated solar power facilities can be integrated with SMR reactors to supply the energy required to produce H2.
Aydin, E. S., & Yucel, O. (2023). Computational fluid dynamics study of hydrogen production using concentrated solar radiation as a heat source. Energy Conversion and Management, 276, 116552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2022.116552
See more at Energy Conversion and Management
SolarPACES Tasks:
TASK II Solar Chemistry
TASK IV Solar Heat Integration in Industrial Processes