Abstract:
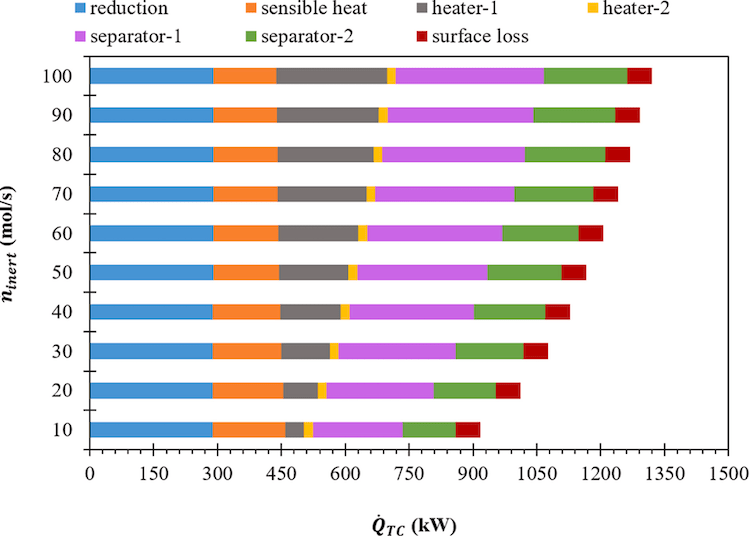
This investigation reports the thermodynamic efficiency analysis of a hybrid ZnSO4/ZnO water-splitting cycle. The data required for efficiency calculations are gathered from HSC Chemistry Software. The prime goal is to examine the effects of the thermal energy needed for heating inert sweep gas and separating the gaseous components in the cycle on the solar-to-fuel energy conversion efficiency. Complete dissociation of ZnSO4 into ZnO, SO2, and O2 is considered. Besides, a comprehensive re-oxidation of ZnO in the presence of SO2 and H2O is assumed. A thermodynamic process model, which includes reduction and oxidation reactors, two separators, multiple gas-to-gas heat exchangers, two heaters, and one ideal H2/O2 fuel cell, is developed and used to analyze the efficiency. The energy required for the separation of inert/O2/SO2 gas mixture is observed to be one of the significant contributors to the energy needed to drive the ZnSO4/ZnO WS cycle. The solar power required (989.9 kW) is recorded to be the lowest for the inert gas molar flow rate equal to 10 mol/s. Because of the low solar energy requirement, the maximum solar-to-fuel energy conversion efficiency (28.4 %) is attained at the thermal reduction temperature of 1445 K.
Bhosale, R. R. (2024). H2 producing hybrid solar thermochemical ZnSO4/ZnO water splitting cycle: Thermodynamic efficiency analysis. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 49, 1584-1592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.11.005