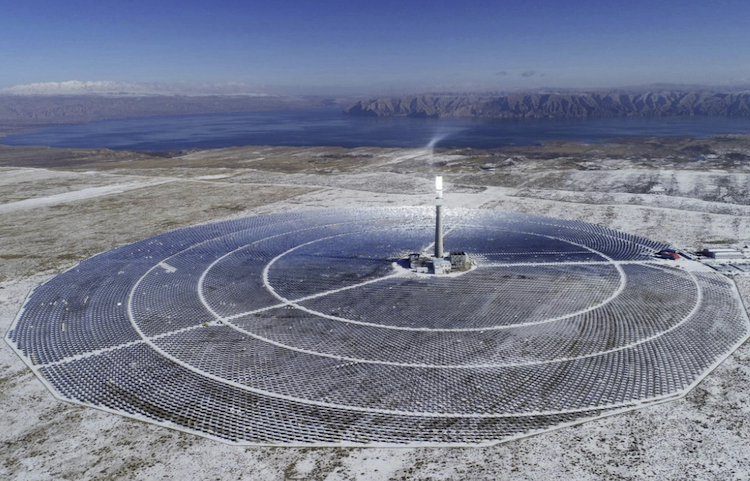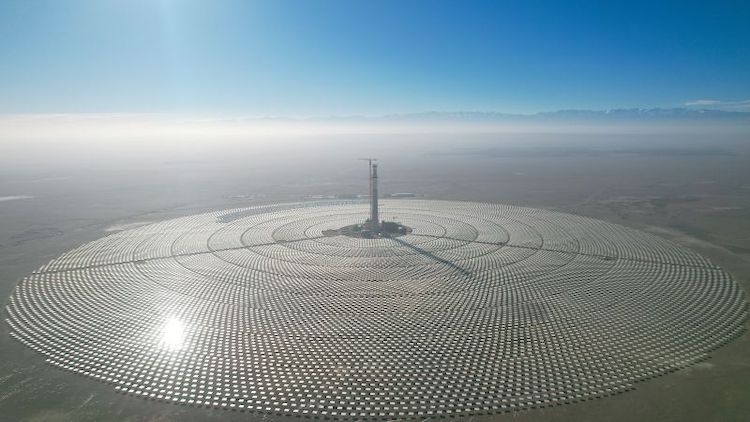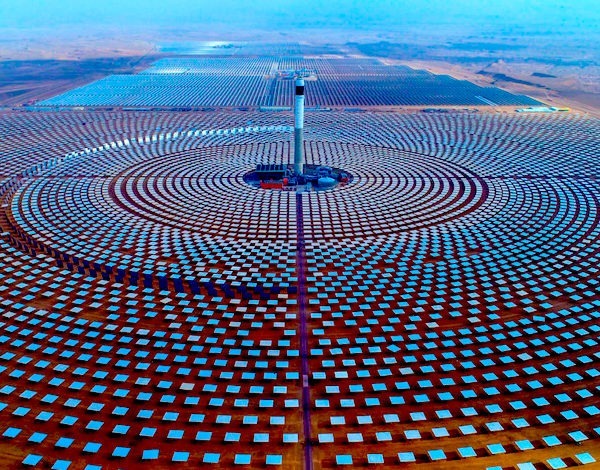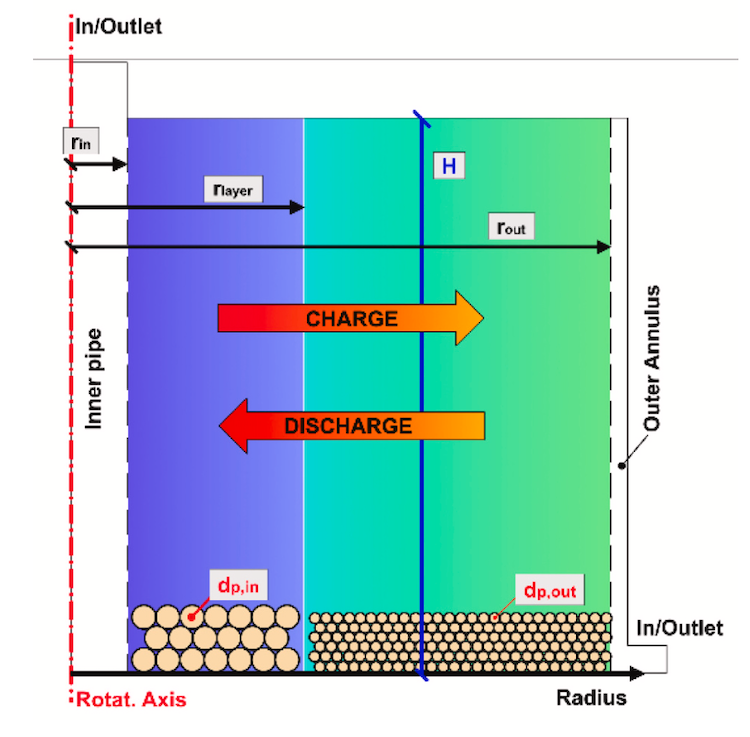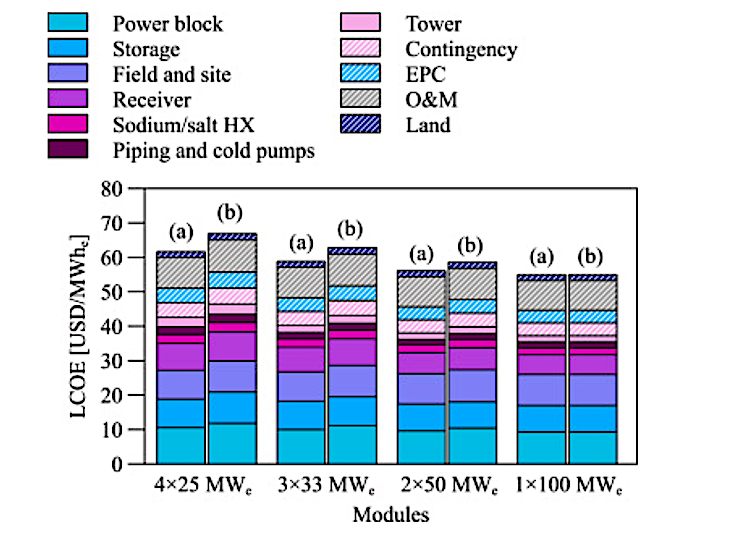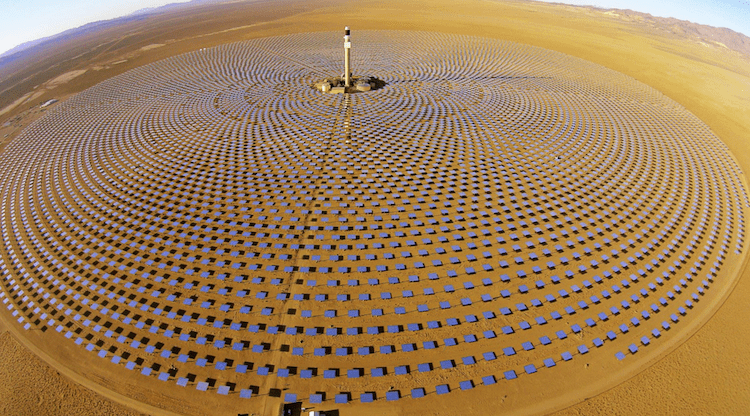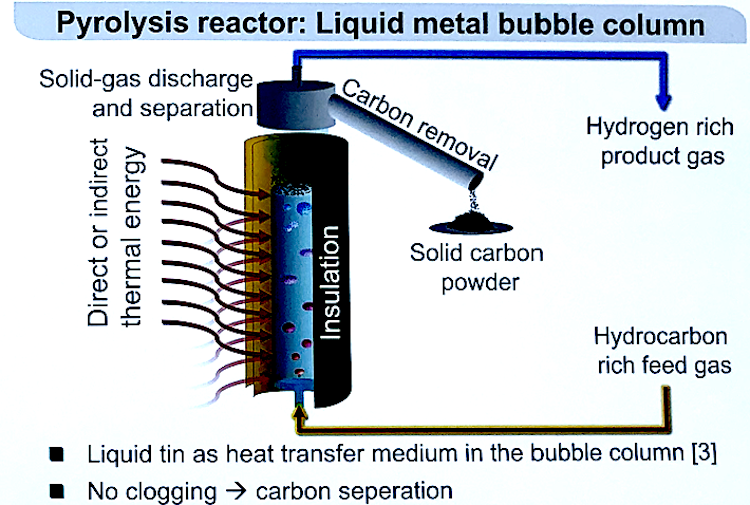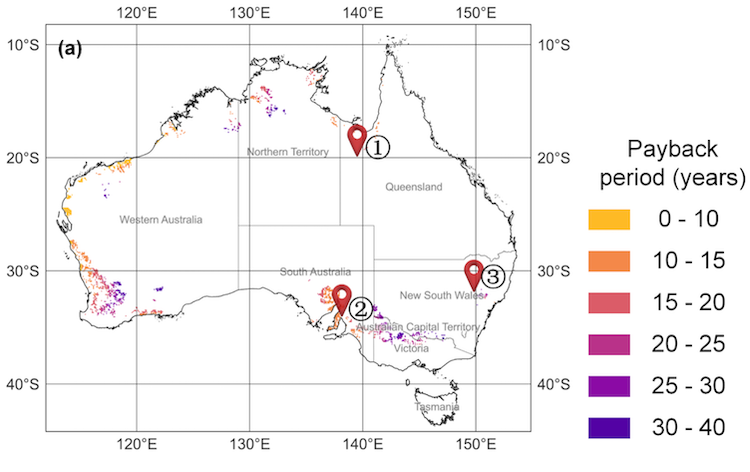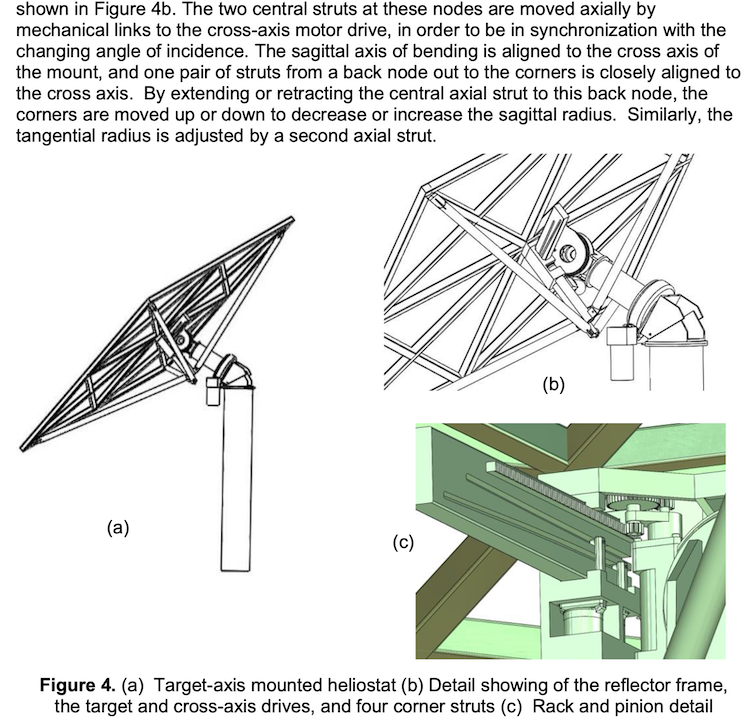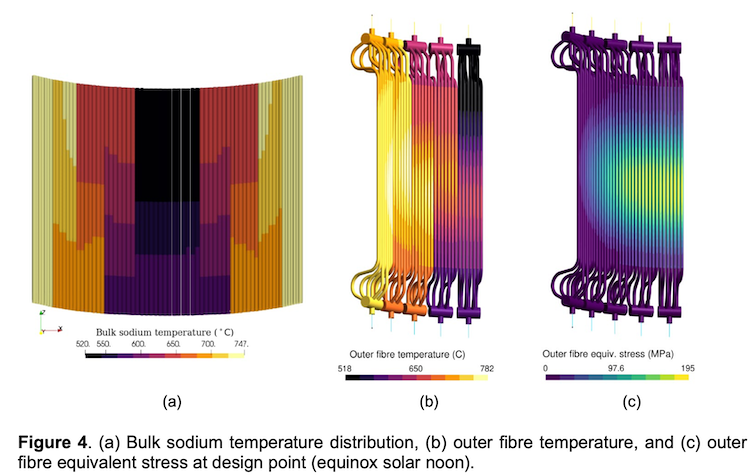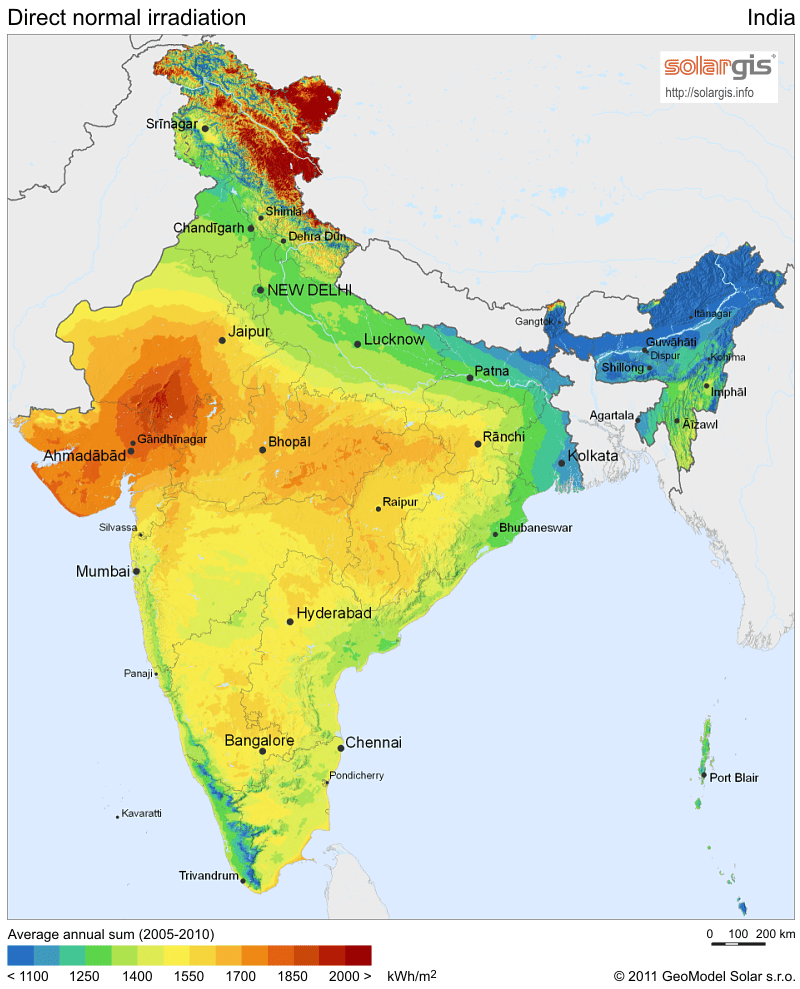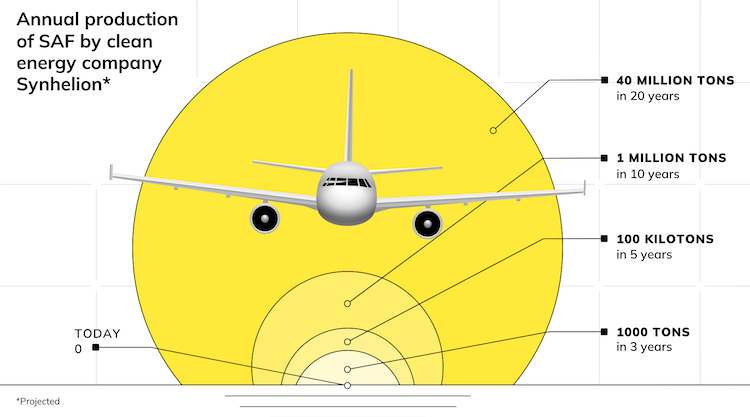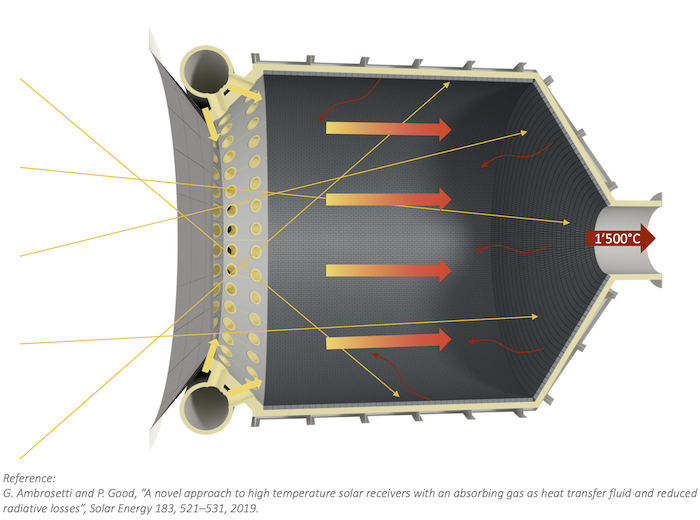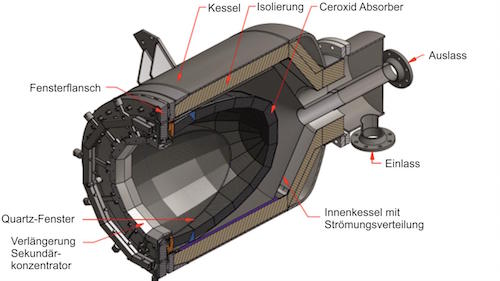
The cost of renewable energy has significantly decreased in recent years, which marks the way towards a fully renewable and sustainable future. However, this energy transition is not possible without massive grid-scale energy storage technology since most of the renewable energies are highly variable. In areas with a high solar resource, Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) can play a crucial role, thus, significant advances are being made to increase its competitiveness through the improvement of the energy storage systems integrated with CSP. The present study provides a comprehensive review on the latest advances and challenges of the most promising energy storage strategies for the next-generation CSP plants, while also addressing the limitations of the state-of-the-art technology. This review includes a thorough analysis of the well-known emerging Thermal Energy Storage (TES) systems to harness solar energy, as well as excess electricity storage systems. The latter includes Power-To-Heat-To-Power (P2H2P) and Compressed/Liquefied Gas Energy Storage (CGES/LGES) technologies for storing low-value excess energy from other renewable energy technologies lacking feasible energy storage options. The study also explores their integration with advanced power blocks. A fair comparison has been conducted taking various factors into account: energy storage density, operating conditions, estimated costs, reliability, cyclic thermal/chemical stability, technical maturity, complexity and efficiency. Although no single technology can fulfill all the requirements simultaneously, the results present promising advances, serving to draw the outline of the future directions and prospects to boost the CSP sector in the upcoming decade.
Baigorri, J., Zaversky, F., & Astrain, D. (2023). Massive grid-scale energy storage for next-generation concentrated solar power: A review of the potential emerging concepts. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 185, 113633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2023.113633