Solar hydrogen testing has begun at the CSIRO test site in Australia.
Tests are underway on a cutting edge renewable hydrogen technology that is being backed by iron-ore billionaire Andrew Forrest to deliver a cheaper and more scalable way to produce the zero emissions fuel using concentrated sunlight.
Sparc Hydrogen – a joint venture majority owned by ASX-listed Sparc Technologies with shares also held by the University of Adelaide (28%) and Forrest’s Fortescue Future Industries (20%) – is developing next generation green hydrogen technology using a process known as photocatalytic water splitting (PWS).
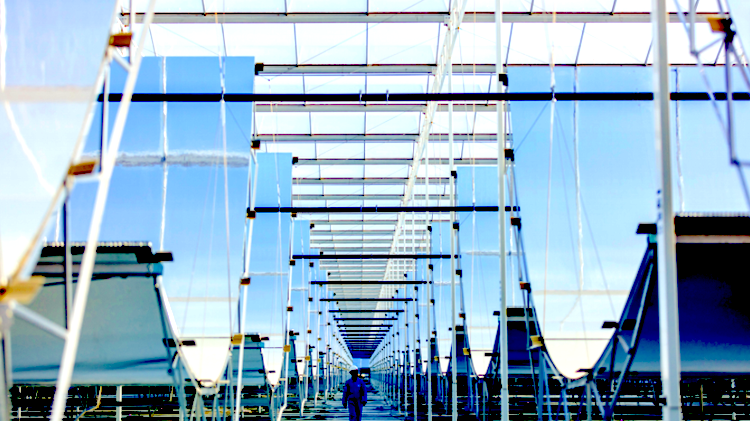
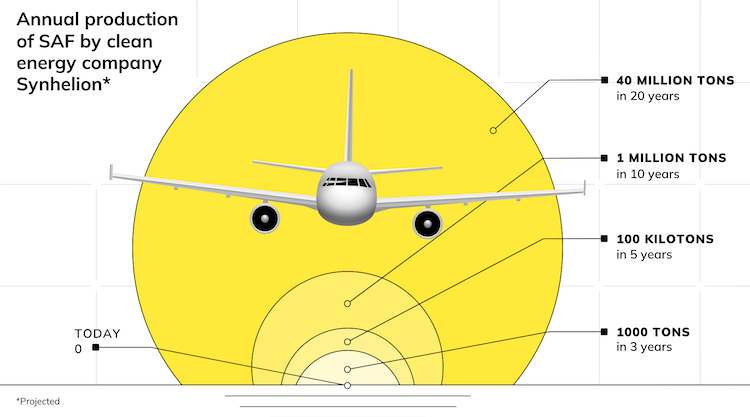
The PWS process offers an alternative to producing green hydrogen via electrolysers powered by vast amounts of renewables, using only sunlight, water and a photocatalyst – in the case of Sparc, using concentrated solar.
The company is now putting this technology to the test with the help – and funding – of CSIRO.
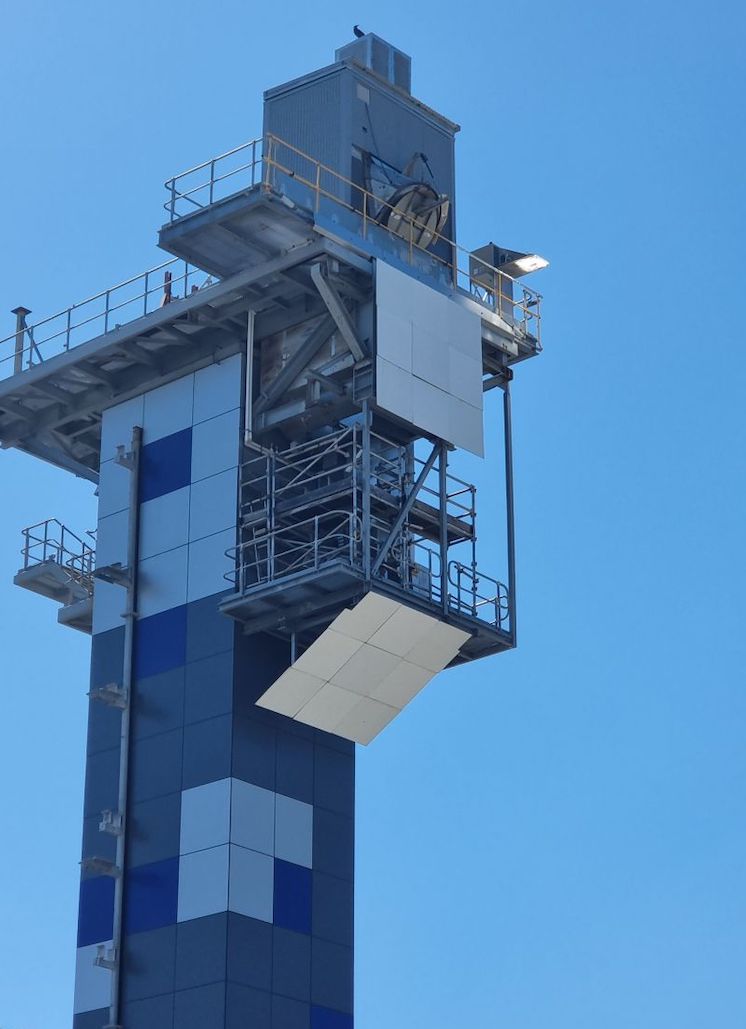
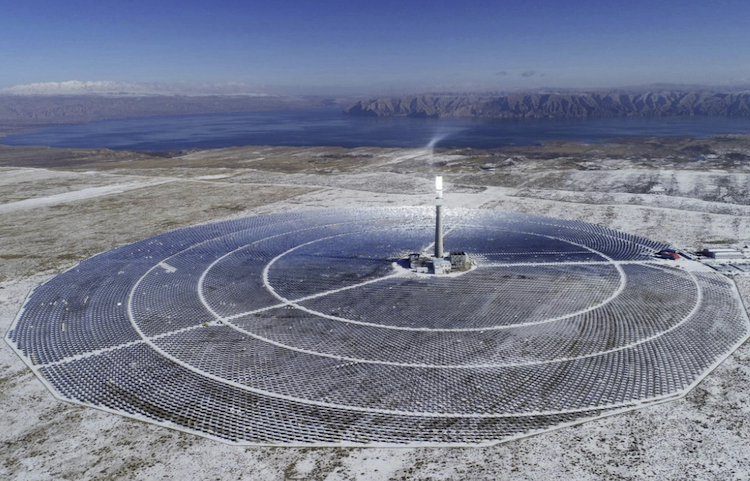
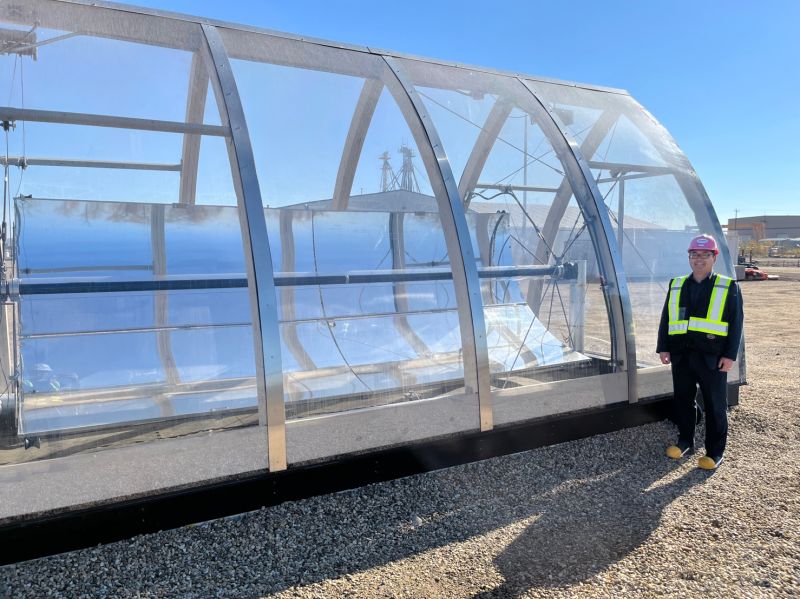
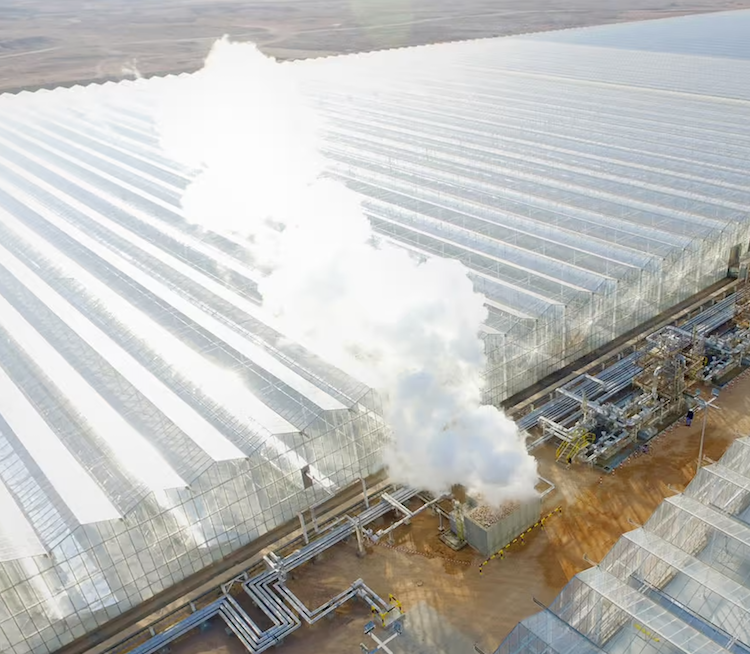
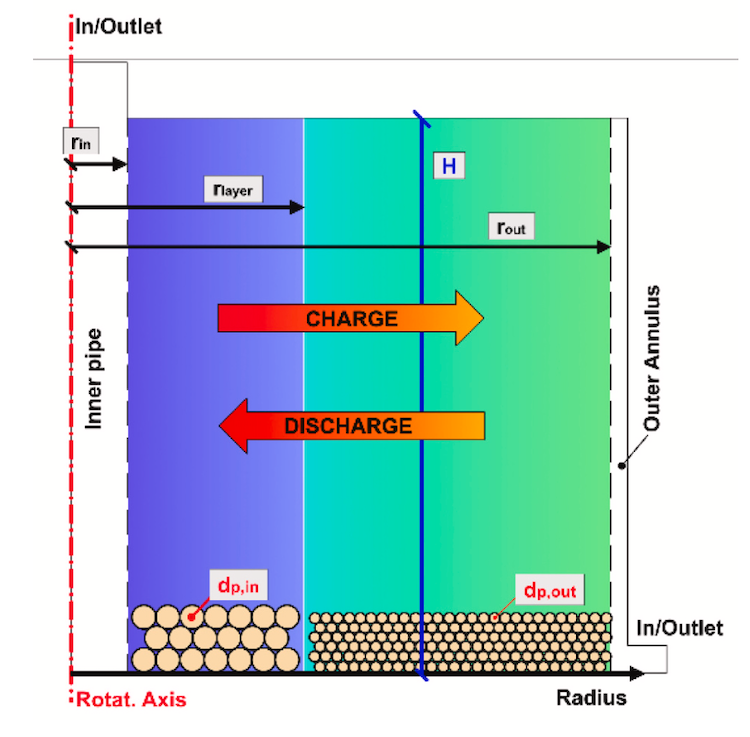
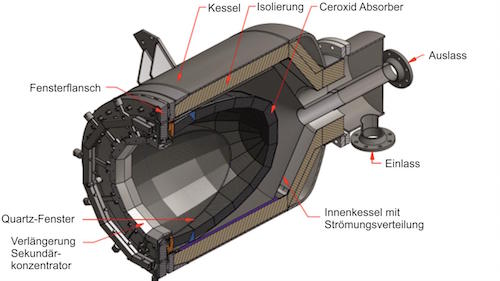
In an update on Thursday, Sparc Hydrogen said a prototype photocatalytic water splitting (PWS) reactor unit has been mounted in place on a solar tower and connected to water, power and communications at the CSIRO Energy Centre in Newcastle, New South Wales.
“Calibration work with the heliostat field and preliminary tests have been completed and the formal testing program commenced on 13 September 2023,” an ASX announcement says. “Sparc intends to update the market upon completion of the testing program.”
The JV says the key goals of the testing are to get the technology a big step closer to being commercially deployable, while also gathering valuable data and information for pilot plant reactor design.
The gathering of “real world” results is also expected to help establish Sparc Hydrogen as a world leading proponent of PWS technology, the company says.

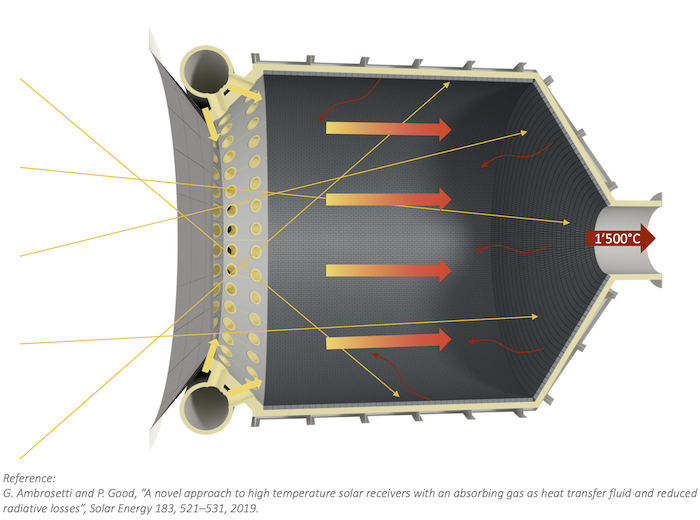
The concentrated solar falling particle receiver seen here reaches the high temperatures used for solar thermochemistry. SolarPACES Conference 2023 will include a site tour here. IMAGE@Wil Gardner, CSIRO
“If the Sparc Hydrogen technology is successful, it could ultimately be used to help produce green hydrogen at a larger and much more affordable scale,” said FFI CEO Mark Hutchinson of the technology last year.
“Our goal is to develop green hydrogen and renewable energy innovations and technology, with a specific focus on decarbonising hard-to-abate industries that can be commercialised fast.”
Sparc Hydrogen has received funding of $28,688 through the CSIRO Kick-Start Program towards the cost of the prototype testing.
Source: Renew Economy
Solar fuels research (IEA Task II) is conducted globally at SolarPACES affiliated institutions like CSIRO around the world