Latest in Development: 2023
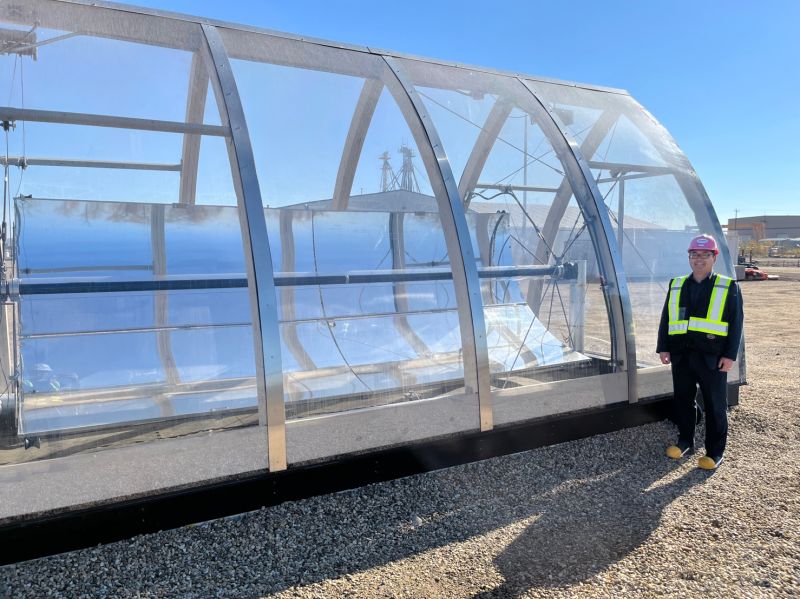
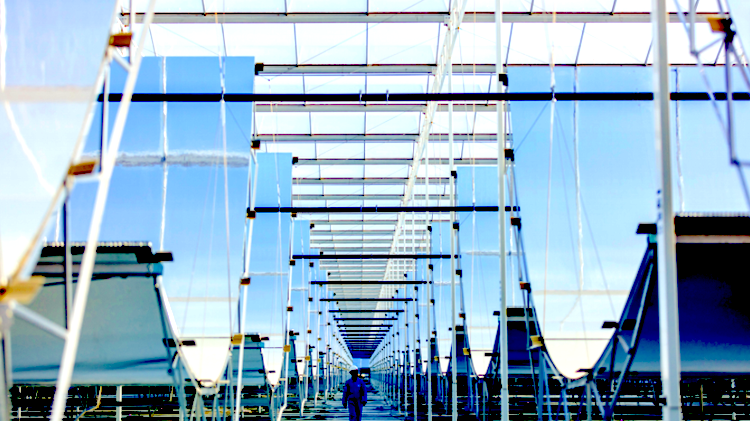
Vast Solar 30 MW CST (solar fuels production)

Groundbreaking is expected in 2024 on Solar Methanol 1 (SM1), a world-first green methanol demonstration plant that will source direct solar heat from the 30 MW Vast Solar (VS1) CST project to supply the solar thermochemistry for green methanol
Latest Online: 2016
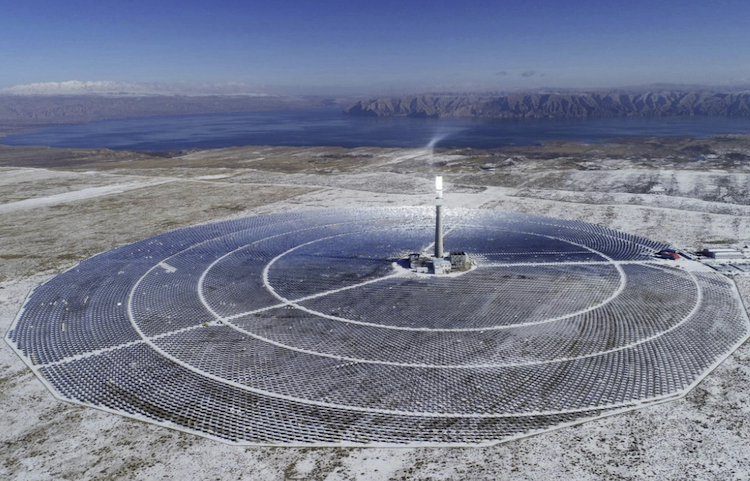
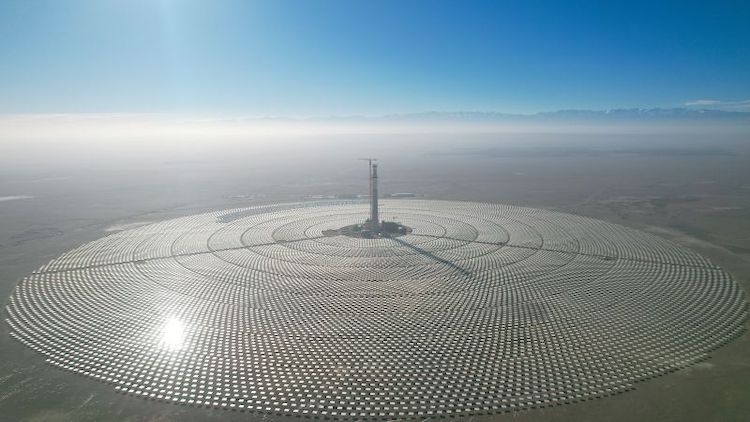
Sundrop Farms 36 MW CST: SolarPACES-NREL database: All plant details on this CSP project
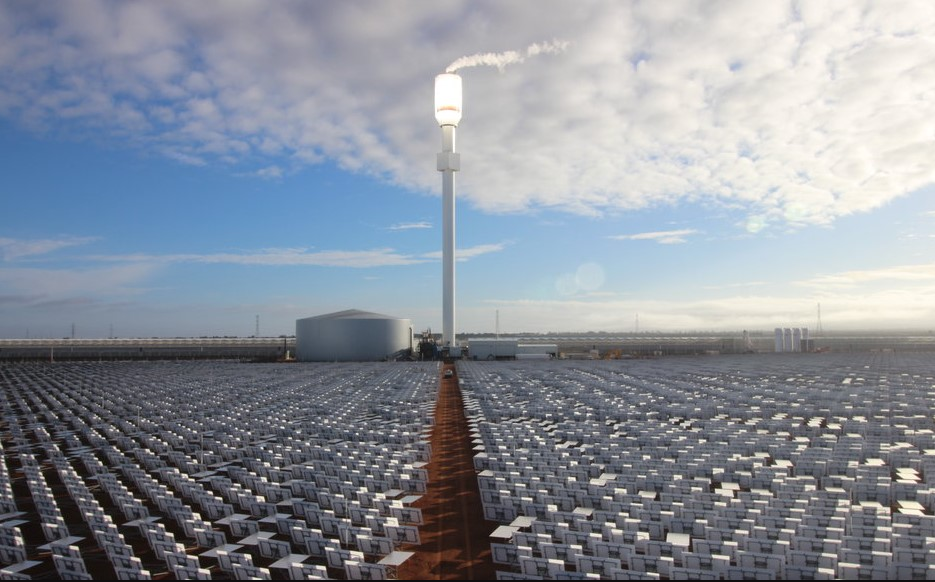

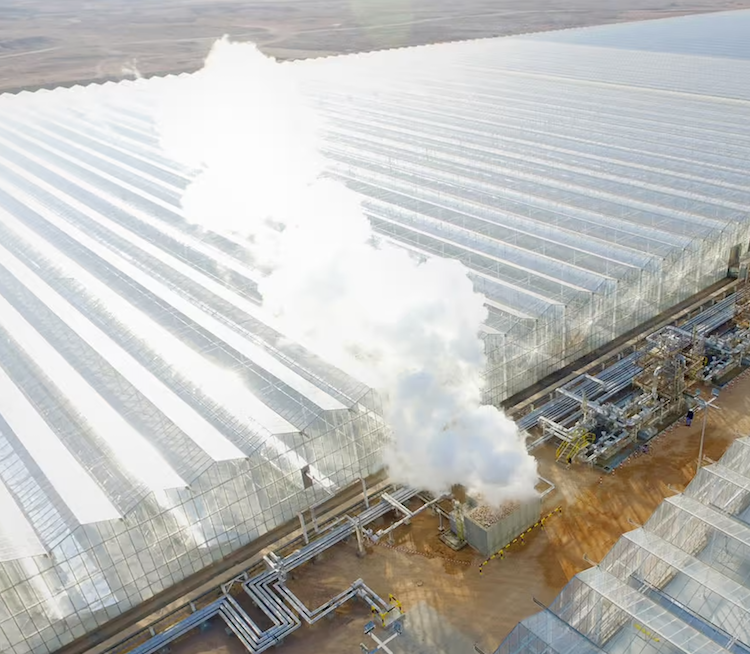
The Sundrop project uses tower CSP for onsite greenhouse agricultural production since 2016. CSP for electricity for heating and cooling, as well as desalination of seawater for crop irrigation.

Earliest Online: 2008
A Fresnel pilot: Novatec 9 MW at Liddel Power Station, where it augmented generation at a 2 GW coal power station, currently not operational (NREL).
CSP Potential
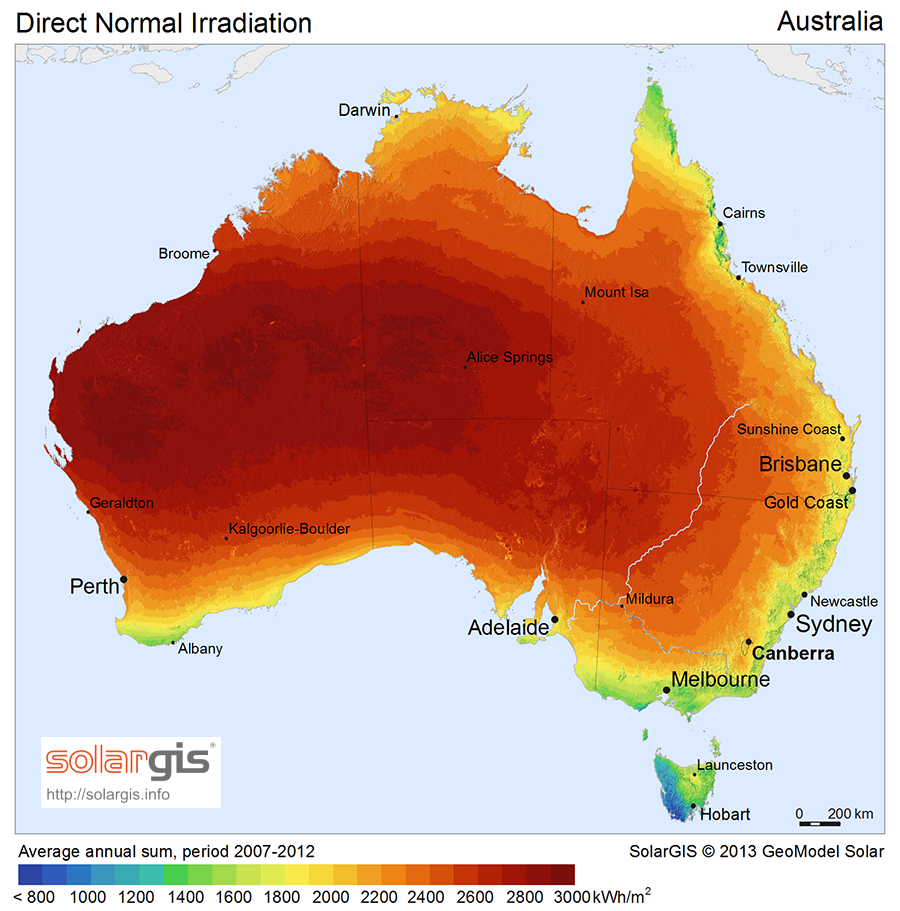
Country Data
| Area |
7,686,849_km2
|
| Population (2012) |
22,683,600
|
| GDP (2011) |
1,371,764 US$ mill.
|
| Installed power capacity (2012) |
50 GW
|
| Electricity consumption (2011) |
252,619 GWh
|
| Generation from RE sources (2011) |
10%
|
| Generation from CSP (2012) |
–
|
| Primary energy production (2009) |
310.7 MTOE
|
| Primary energy net import (2009) |
173 MTOE
|
| Total primary energy supply (2009) |
131 MTOE
|
| Total final consumption (2009) |
77.7 MTOE
|
History of CSP Development
The Australian Government developed in 2001 a plan to move to a clean energy future, the Mandatory Renewable Energy Target (MRET) was aimed for the annual production of 9450 GWh from renewable energy sources by 2010. This target was expanded in 2009 to an additional 45000 GWh per year by 2020 (about 20% of the total Australia’s electricity needs). The plan was renamed Renewable Energy Target (RET).
In 2004, Ausra completed a solar field with about 1 MWe in order to supplement the 2000 MW coal-fired Liddell Power Station and subsequently was increased up to 9 MWth by 2008. This was the world’s first solar thermal power collector system for coal‐fired power augmentation. In December 2010, Novatec Solar was awarded the contract to expand the facility with another 9.3 MWth. This phase was completed by October 2012.
On 10th July 2011, the Australian Government announced the establishment of the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), as part of its Clean Energy Future package. ARENA was created to coordinate around $3.2 billion in existing grant funding programs supporting research, development and demonstration of new renewable energy technologies.
On 1st July 2012, Australia introduced a carbon tax, a price of $23 per tonne of emitted CO2 on selected fossil fuels consumed by major industrial emitters only. The fixed price of $23 is scheduled to rise by 5% per year.
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is leading a program funded with $87 million to drive down the cost of CSP from about 25 to 10-12 cents per kWh.
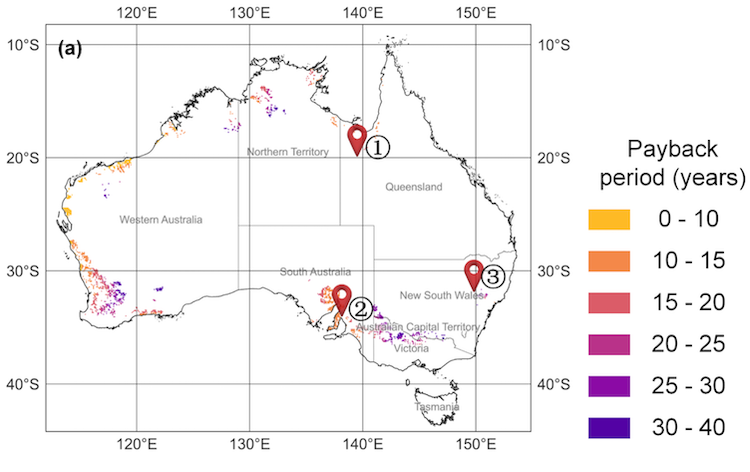
In 2014 Australia had about 8.5 MW of CSP installed (Liddell and Lake Cargelligo) and 44 MW under construction (Kogan Creek Solar Boost). However, Areva’s coal-boosting Kogan Creek Solar Boost was cancelled in 2016 and the small Liddel and Lake Cargelligo projects are no longer in operation.
But since 2016, there have been several promising new beginnings. The world’s first “seawater greenhouse” began operation at Sundrop farms in Port Augusta, using a 36 MW tower CSP plant to heat its greenhouses at night, to desalinate the seawater for its tomato crops and to power onsite electrical needs. A new pilot project; Jemalong, a 1 MW tower project came online with 3 hours of liquid sodium storage.
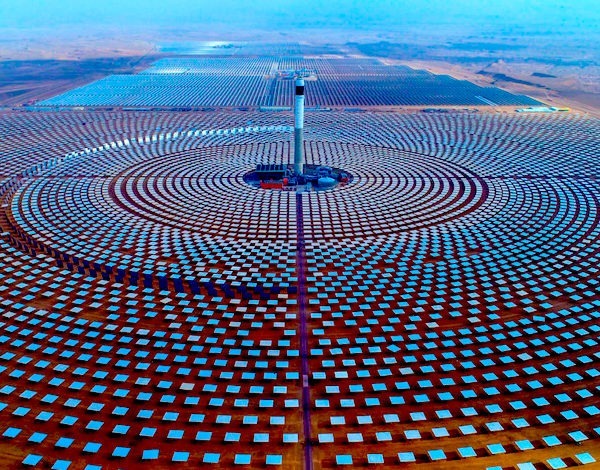
In Port Augusta, very vocal grassroots community support for replacing a now-closed coal power station with CSP with storage, led to international CSP developers proposing state-of-the-art projects at utility-scale, and by mid 2017, SolarReserve won a tender with a bid to build 150 MW tower CSP project by 2020 at a world record contract price of $78 AUD/MWh.
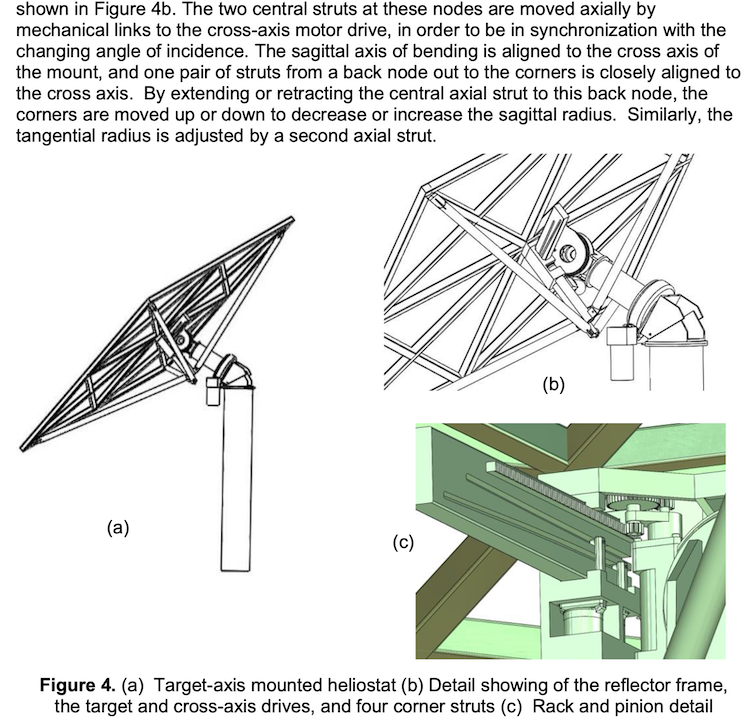
Unable to finance the project, SolarReserve sold the site to Vast Solar, an Australian firm that won the SolarPACES Technology Innovation Award in 2019 for its innovative first use of liquid sodium as a very high temperature heat transfer fluid, that it had tested in a 1MW pilot at Jemalong. It also innovated a new form of CSP, combining elements of both trough and tower, and as of 2023 is developing a new CSP project in the previous SolarReserve site in Port Augusta.
Australia has a focus on industrial decarbonization, both the research and policy level, with close partnerships encouraged at the university level with heavy industries such as mining. Any early example, Sundrop Farms (decarbonizing greenhouse farming in arid conditions) was a innovation breakthrough with global implications.